Learning LWF Chain Graphs: A Markov Blanket Discovery Approach
Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI 2020)
Overview
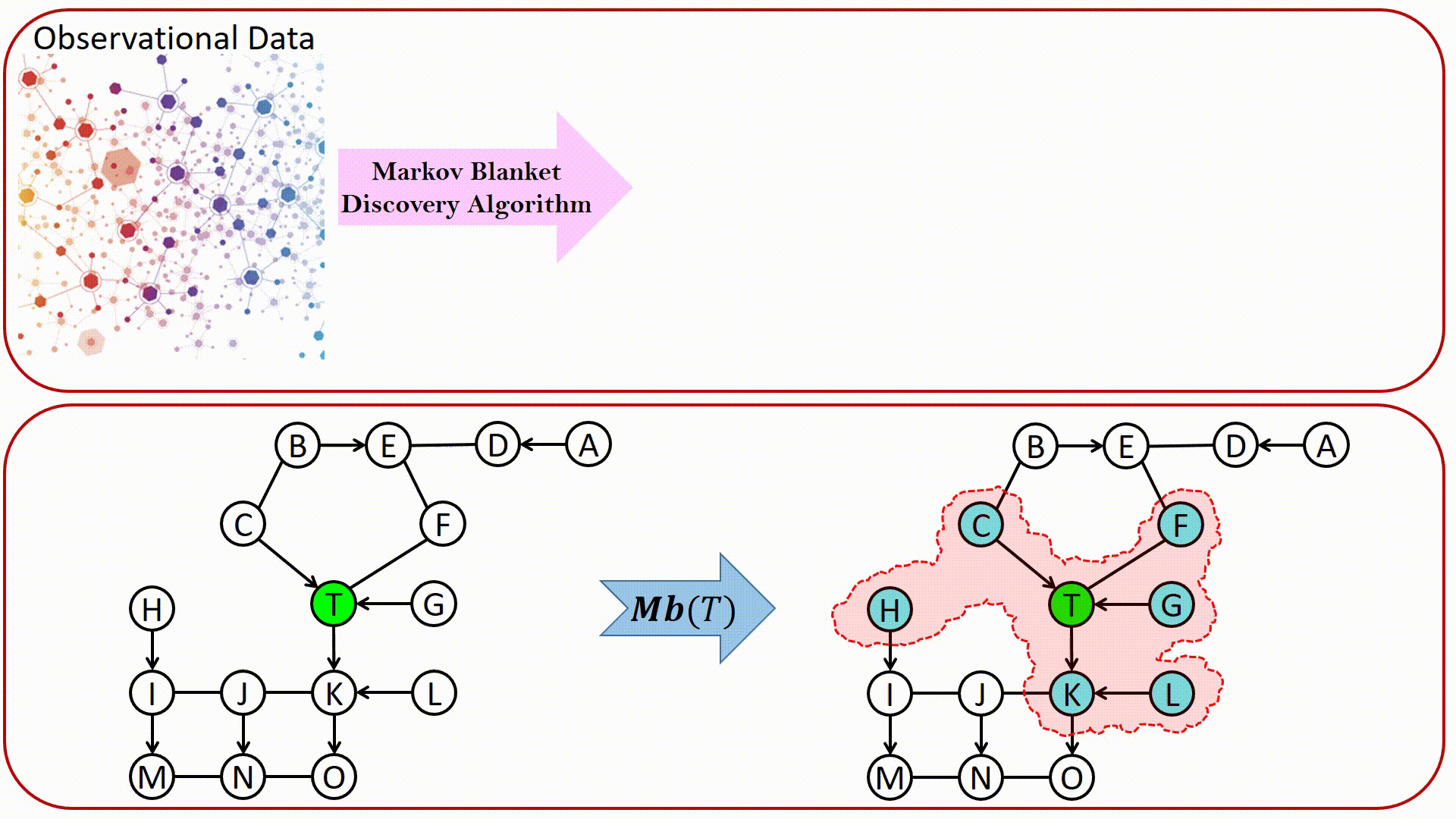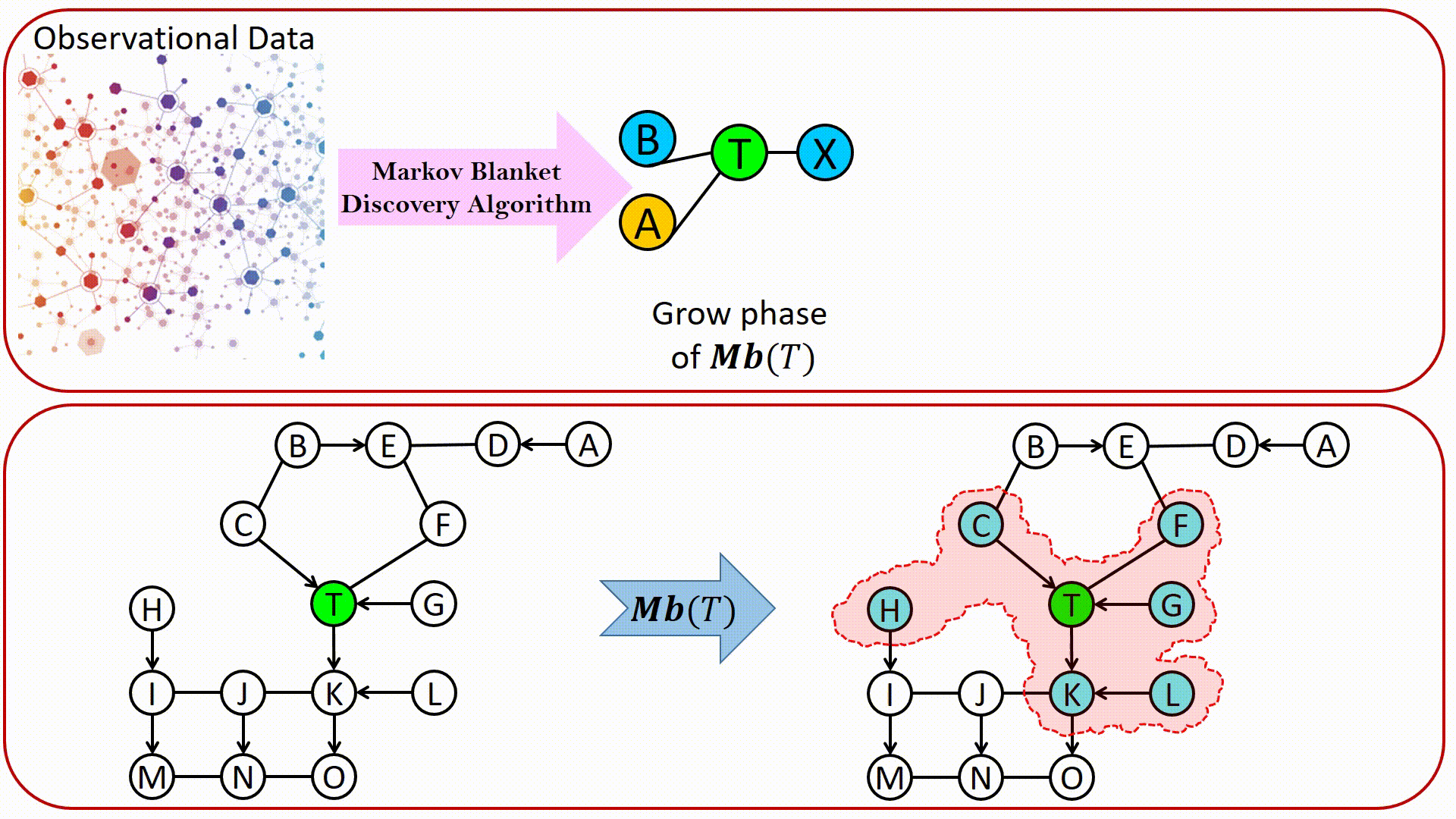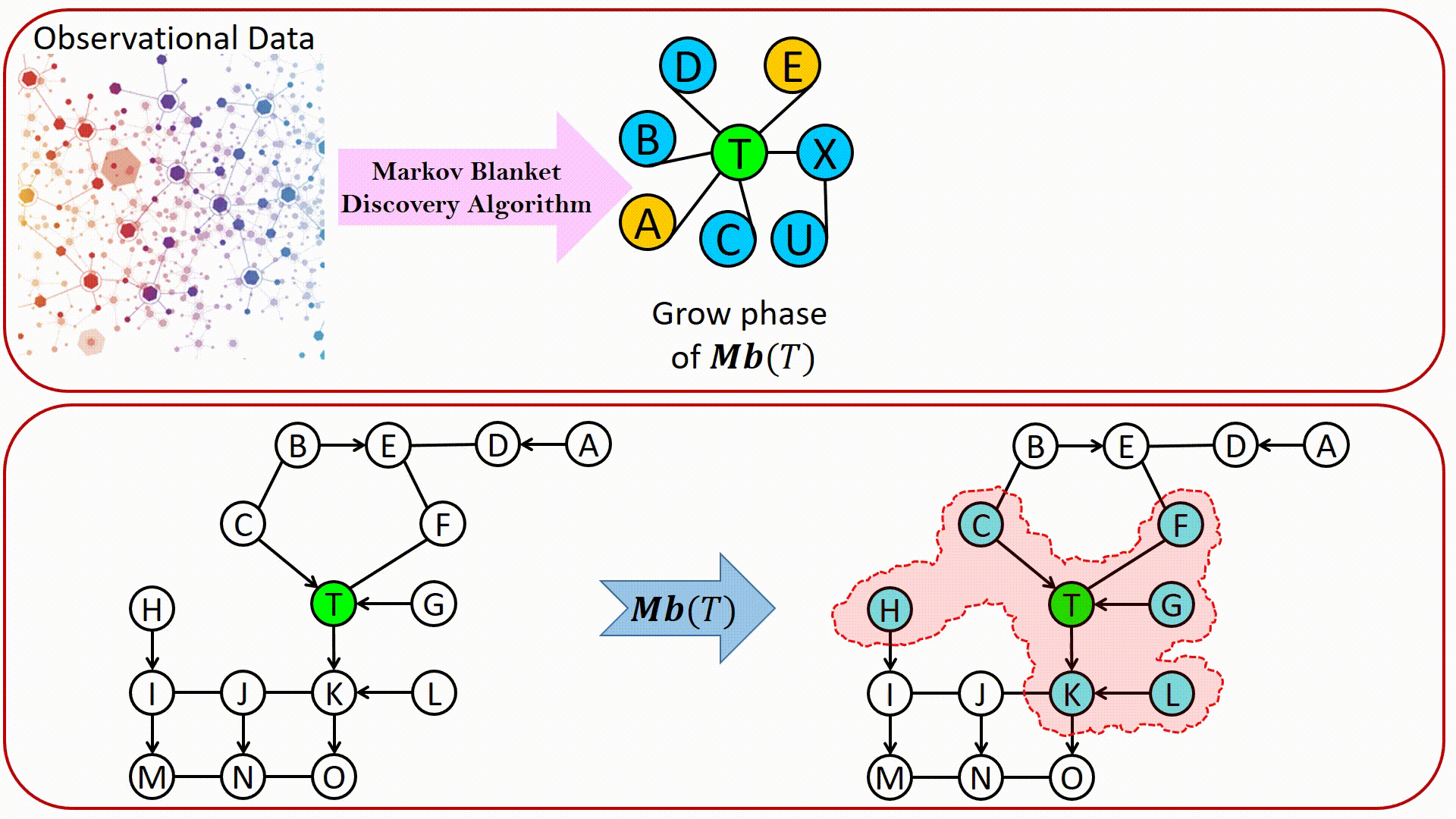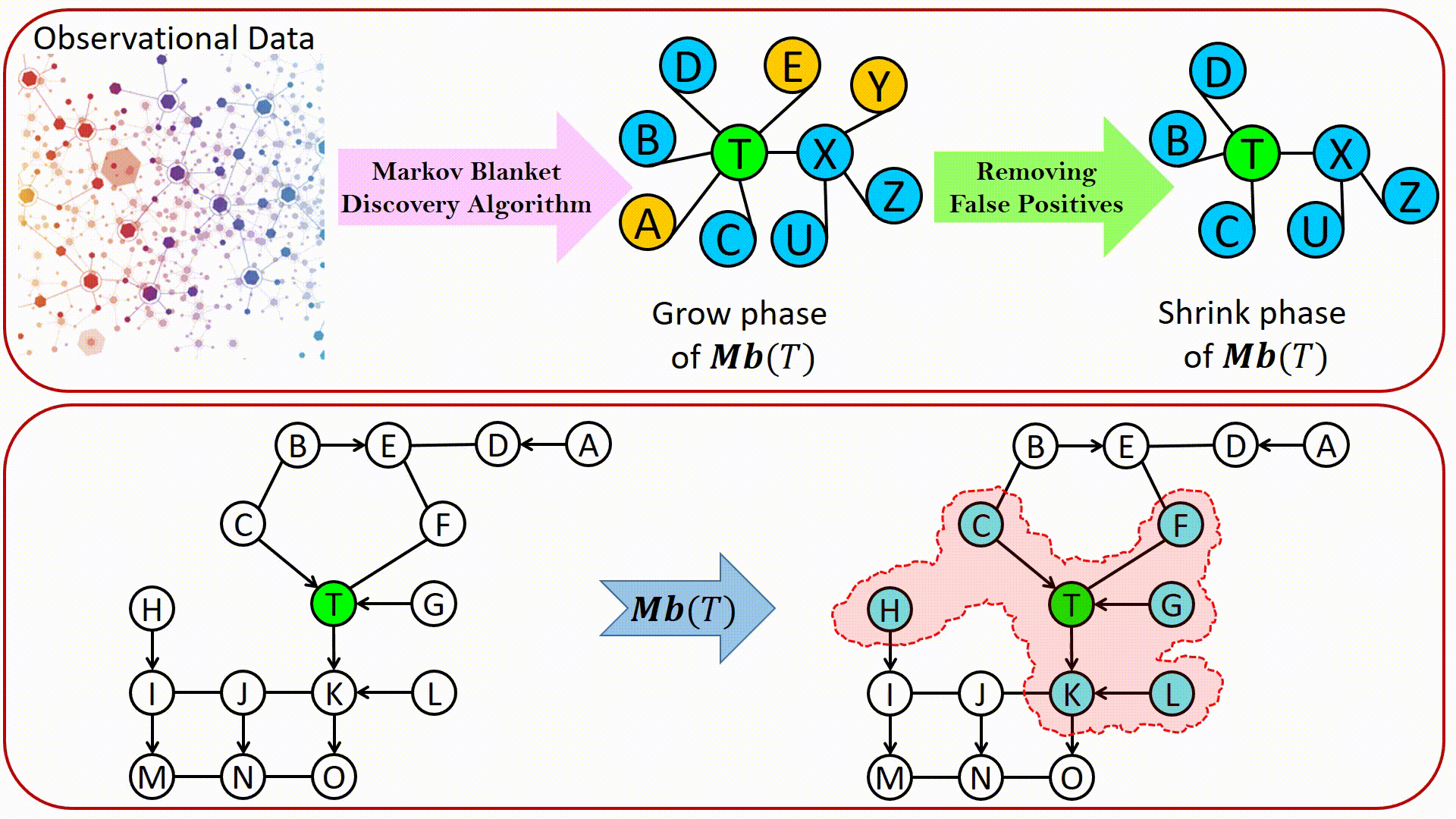
LWF Chain graphs were introduced by Lauritzen, Wermuth and Frydenberg as a generalization of graphical models based on undirected graphs and DAGs. From the causality point of view, in an LWF CG: Directed edges represent direct causal effects. Undirected edges represents causal effects due to interference, which occurs when an individual’s outcome is influenced by their social interaction with other population members, e.g., in situations that involve contagious agents, educational programs, or social networks. The construction of chain graph models is a challenging task that would be greatly facilitated by automation. Markov blanket discovery has an important role in structure learning of Bayesian network. It is surprising, however, how little attention it has attracted in the context of learning LWF chain graphs.
In this work, we provide:
- A graphical characterization of Markov blankets in chain graphs. The characterization is different from the well-known one for Bayesian networks and generalizes it.
- A novel scalable and sound algorithm for Markov blanket discovery in LWF chain graphs.
- A sound and scalable constraint-based framework for learning the structure of LWF CGs from faithful causally sufficient data. With the use of our algorithm, the problem of structure learning is reduced to finding an efficient algorithm for Markov blanket discovery in LWF chain graphs. This greatly simplifies the structure-learning task and makes a wide range of inference/learning problems computationally tractable because our approach exploit locality.
Paper
Mohammad Ali Javidian, Marco Valtorta, and Pooyan Jamshidi. Learning LWF Chain Graphs: A Markov Blanket Discovery Approach in Proceedings of the Thirty Sixth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI-20).
Slides
Code
https://github.com/majavid/MbLWF2020
Talks
Potential Extensions
- Relaxing the faithfulness assumption.
- Addressing the multiple hypotheses testing problem in the small sample case.
- Designing an algorithm for learning ‘latent variable chain graphs (segregated graphs)’ to model interference in relational data.
Acknowledgement
This work has been supported by
- AFRL and DARPA (FA8750-16-2-0042),
- ASPIRE grant from the Office of the Vice President for Research at the University of South Carolina.